
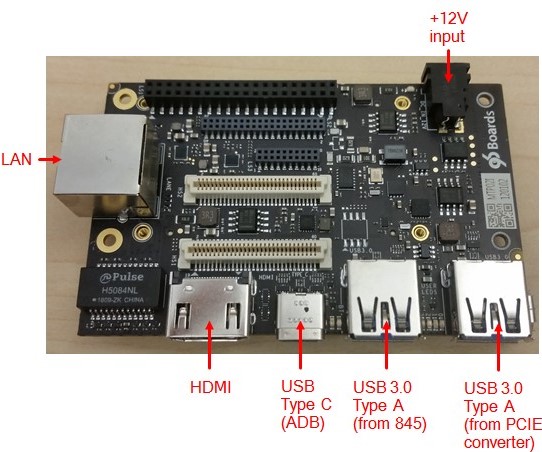
Rebuild Android userspace (see Compiling userspace) andįlash the new kernel (see Flashing images).Dragonboard 845c AOSP support in master has been in a very good state since a while, so it’s time to change my AOSP reference board from the Hikey960 to the Dragonboard and start enabling its phone capabilities.īesides having better specs than the Hikey960, the Dragonboard has an important edge, that is the possibility of having at the same time both host and device capabilities through USB, very useful for debugging issues through adb. If -dist_dir is unspecified, refer to the output of theĬommand for the location of the artifacts.įor details, refer to the Kleaf documentation. Note: The kernel binary, modules, and corresponding images are located in the mkdir repo-common cd repo-common repo init -u -b common-android-mainline repo sync -j8 -c rm -rf out tools/bazel run //common:db845c_dist -dist_dir=$DIST_DIR

Run following commands to clone the kernel source and prebuilt Android To build the DragonBoard db845c Android Generic Kernel Image (GKI) kernel artifacts: device/linaro/dragonboard/installer/db845c/recovery.sh Building the kernel If necessary, you can perform QDL board recovery by running the following scriptĪfter booting db845c in USB flashing mode (see DragonBoard device/linaro/dragonboard/installer/db845c/flash-all-aosp.sh build/envsetup.sh lunch db845c-userdebug make -j24 device/linaro/dragonboard/fetch-vendor-package.shīuild AOSP. Use the following commands to download and build Android on the DragonBoardĭownload the Android source tree: repo init -u -b master repo sync -j8ĭownload the current vendor package.
The DragonBoard 845c is part of the RB3 platform and is available fromįigure 1. Kernel development, and perform other tasks with fewer OEM encumbrances. These boards, so developers can easily create and debug peripheral drivers, do AOSP provides kernel source and board support for Khadas VIM3 and Qualcomm Robotics Board RB5Īndroid reference boards. Google supports DragonBoard 845c, HiKey 960, Upgrade efforts, reduce time to market for new Android devices, lower deviceĬosts by enabling ODM/OEMs to choose from a wider range of compatibleĬomponents, and increase the speed of innovation among component suppliers. You can also create builds for DragonBoardĪndroid reference boards, which are designed to help nonmobile component vendorsĭevelop and port drivers to Android releases. For availableĪndroid builds and targeted devices, see Source code tags and Project (AOSP) builds and the relevant hardware-specific binaries. You can create builds for Nexus and Pixel devices using Android Open Source


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
